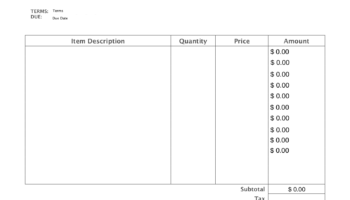
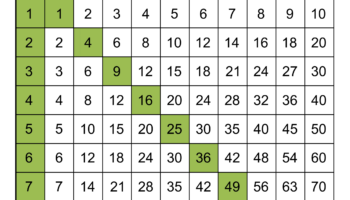
A two-dimensional pattern, capable of being physically produced on a substrate such as paper, and designed to be folded and assembled into a three-dimensional cube. This pattern often includes markings for folding lines and adhesive application areas to facilitate accurate construction. As an example, consider a design featuring six connected squares; strategically folding along the shared edges and securing the final edge creates a solid cube.
The availability of such patterns offers several advantages. It presents a cost-effective means of generating cube-shaped structures for diverse purposes, ranging from educational demonstrations of geometric principles to crafting personalized gift boxes. Historically, these patterns have served as accessible tools for teaching spatial reasoning and developing fine motor skills. Their adaptability makes them useful across various fields.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific aspects of creating and utilizing these patterns, including design considerations, printing techniques, assembly methods, and diverse applications within different contexts. It will also cover the advantages and disadvantages of commonly used designs and assembly practices.